Wednesday, May 24, 2023
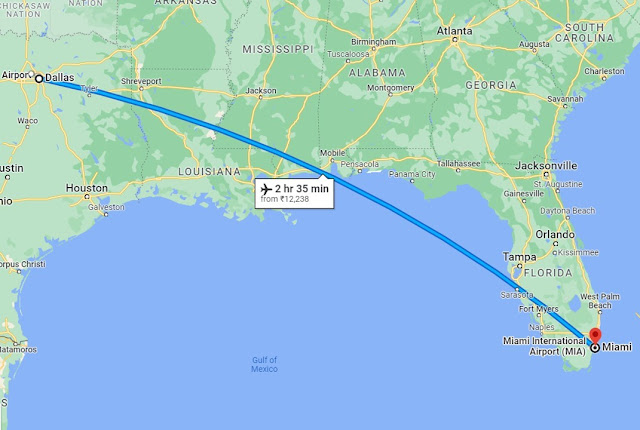
5 Days On Road From Miami To New York
Historical Heritage Of Goa
 |
| Arambol beach |
 |
| Petroglyphs of Usgalimal on the Banks of River Kushavati |
 |
In 1986, 7 Goan Churches and Convents were included in the UNESCO World Heritage Sites since they "are outstanding examples of an architectural ensemble which illustrates the work of missionaries in Asia" - Source: UNESCO website (clockwise on the Map) 1. Chapel of St. Catherine of Alexandria 2. Church of Cajetan 3. SE Cathedral 4. Church and Convent St. Francis of Assisi 5. Basilica of Bom Jesus 6. St Augustine Tower (remains of St. Augustine Church) 7. Church of Our Lady of the Rosary |
8300 BCE, Upper
Palaeolithic to Mesolithic age
1200 BCE, Iron Age:
Between 322 and 185 BCE Mauryans ruled over this part of India. Mauryans were great patrons of Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, and the Ajivikas. Archeological excavations have brought into prominence many Buddhist caves, and Jain and Hindu temples all across Goa.
Between, 50 BCE, mid-1st century BCE and 250 CE Early 3rd
century CE (approx.), the Satavahanas ruled over Goa. The Satavahanas developed maritime trade with Coastal European countries. European-turned-Buddhists moved to India. Greco-Buddhist art and architecture thrived during this period.
Around the 4th century AD, the Bhojas took hold of Goa. They were patrons of Buddhism and Greco-Buddhist art and architecture.
Medieval period:
From the 10th to 14th century CE Kadambas ruled over Goa. They introduced the Kannada language to Goa
Between 1347 and 1518 Bahamani Sultanate took over Goa. They brought Muslim influence to Goa.
Between 1336 and 1646 Vijaynagar Empire brought back southern influence.
Between 1489 and 1510 Adil Shah of Bijapur Sultanate made a second capital at Velha Goa (Old Goa)
In 1510, Vasco Da Gama landed in Calicut, eventually arrived at Goa, and established 450-year rule of the Portuguese in Goa. The Portuguese introduced Christianity To Goa. They built many Churches and Convents with Roman and catholic influence.
In 1961 Indian Army annexed Goa into Indian territory and created the Union territory of, Goa, Daman, Diu
In 1987 Goa gained recognition as an Independent state post the Konkan agitation.
 |
| Heritage Sites of National Importance in Velha Goa (Old Goa) |
 |
| There are 51 heritage sites that are protected by the Archaeological Survey of India marked in blue, yellow, and cyan |
 |
| St Augustine Tower |
 |
| The Aguada fort |
 |
| The Lamgau Caves |
 |
| The Surla Mosque |
 |
| The Mangueshi Temple |
 |
| The Shantadurga Temple |
 |
| The Beach Cottage we stayed at for Rs. 400 a day |
Monday, May 1, 2023
Stepwells (Baolis) Of Delhi
 |
| Agrasen ki Baoli, A 14th-century step-well was built by King Agrasen. |
Purana Qila Baoli (left) is a 16th-century stepwell built by Ruler Sher Shah Suri. Wazirpur Gumbad Baoli (right) was supposedly built during the reign of the Lodi Dynasty between 1451 and 1526. The actual details are still unknown.
Wednesday, April 19, 2023
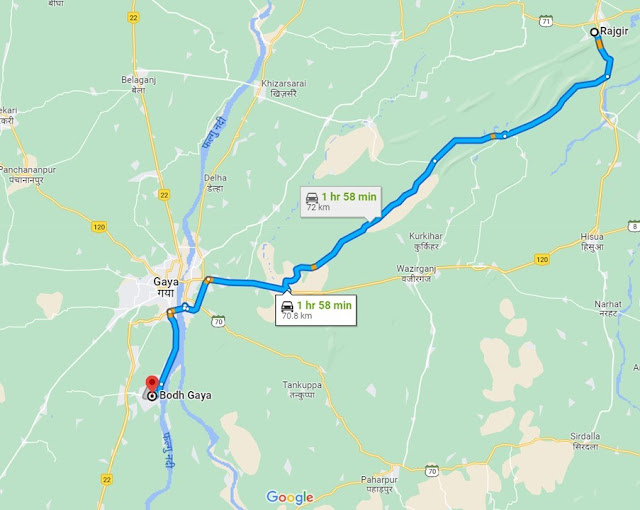
A 5 Day Bihar Excursion
Day 1: Drive to Rajgir
Interesting Case Of Chandigarh
Chandigarh is the only city in India that is a Union Territory, and the Capital of two states, Punjab and Haryana. Curiosity led me to research the topic, of why was Chandigarh made the capital of two states. There are many articles on it, here's mine.
Before partition, the state of Punjab included the states of Himachal Pradesh and Haryana and Lahore was its capital. After the India-Pakistan partition in 1947, Punjab was divided into West Punjab and East Punjab. West Punjab went to Pakistan and East Pakistan went to India.
Why was Punjab divided in 1947?
Punjab like Bengal had a slightly higher majority of Muslims than Hindus (about 53%: 47%). Muslim League demanded both Bengal and Punjab be given to Pakistan considering the majority. Congress contested that the majority was too insignificant. Eventually, it was decided, that Both Bengal and Punjab will be divided. Both partitions led to tragic massacres and are marked as the darkest history of India.
Why was Punjab not divided after partition?
After partition, the first Prime Minister of independent India, J. Nehru, decided not to divide Punjab, since the 1947 partition had already seen a lot of bloodshed and displacement considering there was a religious divide (Sikhs vs Hindus) as well other than the language divide (Punjabi vs Pahari vs Hindi).
Creation of Chandigarh
Since Lahore went to Pakistan, a new capital was needed. It was the first planned city of Independent India. The city was designed by Swiss-French Architect Le Corbusier.
Why was Punjab divided in 1966?
Due to political pressure, and the Sikh agitation for a separate state, Prime Minister I. Gandhi acceded to the proposal of a division. New states of Haryana and Himachal Pradesh were created. Himachal opted for Shimla as its capital. However, Punjab and Haryana contested for Chandigarh. A plebiscite was held and Chandigarh got voted as Hindi speaking majority. Punjab contested the results. Eventually, PM I. Gandhi gave Chandigarh the status of a Union Territory and granted it special status as the capital of two states.
During PM R. Gandhi's term, in 1985 the Longowal Accord was signed which among other conditions, stated Chandigarh would be given to Punjab in exchange for Hindi-speaking cities and villages to Haryana. Soon after Longowall was assassinated, unrest and terrorism engulfed the then-political scene in India. The exchange finally never took place and the status of Chandigarh remains the same to date.
 |
| Source: https://www.mapsofindia.com/maps/india/prepartitionmap.htm |